I. Introduction to Nerve Health
A. Understanding the Nervous System
Your nervous system is like your body’s command centre, controlling everything from your movements to how you feel. It’s divided into two main parts:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): This includes your brain and spinal cord, which process and interpret sensory information.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): These are the nerves that run throughout your body, connecting the CNS to your muscles, skin, and organs.
Nerves send signals that make your body work smoothly, whether it’s lifting your arm or feeling a gentle breeze on your skin. This intricate network is responsible for ensuring every organ and muscle works harmoniously, adapting to both voluntary and involuntary functions. From reflex actions to complex cognitive processes, your nervous system operates seamlessly when healthy.
B. Why Nerve Health Matters
- Everyday Functions Depend on It: Healthy nerves are essential for basic actions like walking, talking, and feeling sensations.
- The Consequences of Nerve Damage: Damaged nerves can disrupt these functions, causing pain, loss of sensation, or other serious problems.
Nerve health is critical for maintaining independence and quality of life. When nerve damage occurs, it can lead to debilitating symptoms, ranging from mild discomfort to severe disability. Early detection and care are essential to prevent irreversible complications.
C. What Can Cause Nerve Damage?
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, excessive alcohol use, or exposure to toxins can harm your nerves.
- Medical Conditions: Diabetes, autoimmune diseases, or infections are common culprits.
- Injuries and Trauma: Accidents or repetitive strain can compress or damage nerves, leading to long-term issues.
Environmental exposures, such as toxins and prolonged mechanical stress, can also damage nerves. Chronic diseases, like diabetes, often silently affect nerve health over time, making prevention and regular health checks even more vital.
II. Physical Symptoms of Nerve Health Issues
A. Numbness and Tingling
- What It Feels Like: A pins-and-needles sensation or total numbness in your hands or feet.
- Possible Causes: Diabetes, vitamin deficiencies, or compressed nerves from injuries.
- Who’s at Risk? People with certain medical conditions, desk jobs, or repetitive strain injuries.
This symptom can start subtly, affecting small areas, but may expand if the underlying cause is not addressed. Persistent tingling may signal serious nerve damage, highlighting the importance of early intervention.
B. Muscle Weakness
- Signs of Weakness: Struggling to lift objects or feeling unsteady.
- Linked Conditions: Neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis or ALS.
- Why Early Detection Matters: Catching it early can prevent the problem from getting worse.
Muscle weakness can progress quickly, affecting balance and coordination. This often leads to secondary issues such as joint strain or falls. Addressing the root cause promptly can prevent these complications.
C. Pain and Discomfort
- Types of Pain: Nerve pain can feel sharp, burning, or shooting.
- Chronic vs. Acute: Chronic pain sticks around, while acute pain is temporary.
- Managing Pain at Home: Light exercise, heat therapy, or over-the-counter remedies can help.
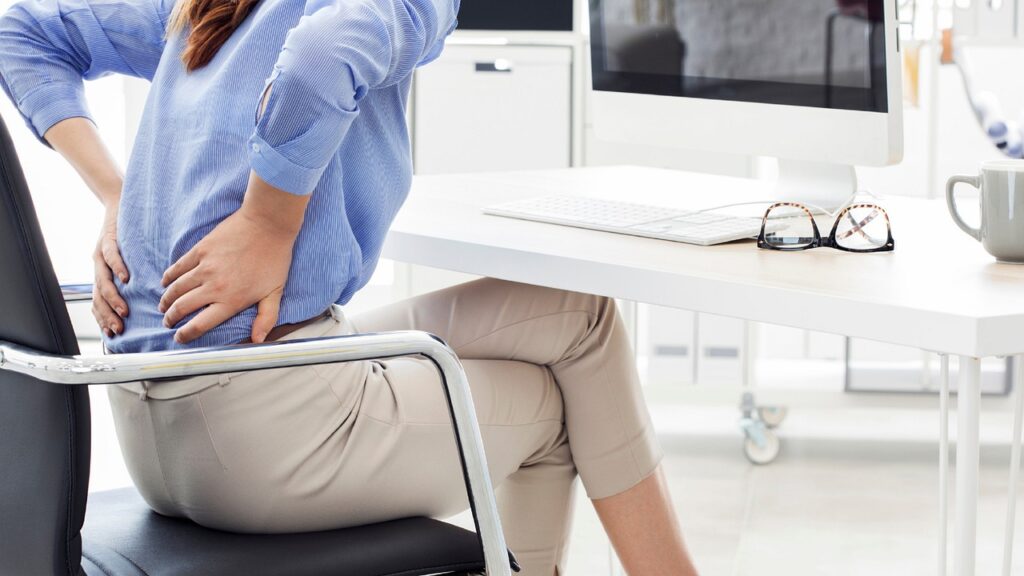

Untreated nerve pain can have a cascading effect, impacting sleep, mental health, and overall quality of life. Seeking professional advice for persistent pain can lead to better management options and relief.
III. Changes in Sensory Perception
A. Altered Touch Sensitivity
- What It Means: Difficulty distinguishing textures or feeling pressure.
- Why It Happens: Conditions like nerve compression or neuropathy.
- Impact on Life: This can make everyday tasks, like holding objects, harder than they should be
These changes can indicate underlying health problems, including diabetes or spinal disorders. Reduced touch sensitivity can also increase the risk of injury, as pain or pressure might go unnoticed.
B. Vision and Hearing Issues
- How Nerves Are Connected to Senses: The optic and auditory nerves are crucial for sight and hearing.
- Red Flags: Blurred vision, ringing in your ears, or hearing loss.
- When to Get Help: If these issues persist, see a healthcare provider.
Vision and hearing problems linked to nerve damage may be early warning signs of neurological conditions. Regular eye and hearing exams can help catch these problems early.
C. Changes in Taste and Smell
- How Nerves Affect These Senses: Sensory nerves in your brain control taste and smell.
- Common Causes: Infections, medications, or nerve damage.
- Why It Matters: Sudden changes might signal underlying nerve problems.
Losing these senses can affect appetite and nutritional health. Addressing these changes promptly can restore quality of life and uncover potential health issues.
IV. Cognitive and Emotional Indicators
A. Memory and Focus Problems
- Nerve Health and Cognitive Function: Nerves help you think, remember, and concentrate.
- What’s Normal vs. What’s Not: Some forgetfulness is normal with age, but persistent issues could be nerve-related.
- Why It’s Important to Act: Early intervention can help slow or stop cognitive decline.
Cognitive issues can disrupt daily life and work performance. Understanding the link between nerve health and brain function highlights the need for mental stimulation and medical care.
B. Mood and Behavior Changes
- The Mind-Body Connection: Nerve health influences emotional well-being.
- Warning Signs: Increased anxiety, depression, or mood swings.
- How to Cope: Therapy, mindfulness, and medical support can make a big difference.
Emotional changes may signal deeper issues, including chronic stress or systemic nerve disorders. A holistic approach to emotional and physical health can promote overall well-being.
Consider using products designed for nerve repair. Find out more.
C. Sleep Problems
- Nerve Issues and Sleep: Pain or discomfort from nerve problems can interrupt your sleep.
- What to Watch For: Trouble falling or staying asleep.
- How to Improve Sleep: Stick to a schedule, practice relaxation, and address underlying nerve issues.
Chronic sleep disruptions can weaken the immune system and exacerbate nerve problems. Identifying triggers and adopting good sleep hygiene can help break this cycle.
V. Preventing and Managing Nerve Health Issues
A. Healthy Lifestyle Habits
- Exercise Regularly: Movement improves blood flow and supports nerve health.
- Eat for Your Nerves: Foods rich in B vitamins, omega-3s, and antioxidants help keep your nerves healthy.
- Avoid Harmful Substances: Cutting down on alcohol and quitting smoking can reduce the risk of nerve damage.
Incorporating mindfulness practices like yoga or meditation can also support nerve health by reducing stress and inflammation, which are known to affect nerves negatively.

B. Regular Check-Ups
- Why They Matter: Routine screenings can catch nerve problems early.
- Common Tests: Doctors may use electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies.
- Speak Up: Don’t hesitate to share any symptoms with your doctor.
Regular health checks ensure that minor symptoms don’t escalate into severe issues. Open communication with healthcare providers is key to effective treatment.
C. Treatment Options
- Traditional and Alternative Therapies: Medications, physical therapy, and even acupuncture can help.
- Rehabilitation: Therapists can guide you through exercises to regain function.
- Stay Monitored: Regular follow-ups ensure your treatment plan is working.
Emerging therapies, like nerve regeneration research, offer hope for the future. Staying informed about advancements can open up new possibilities for treatment.

